Conserving Biodiversity
Conservation biology matured in the mid- 20th century as ecologists, naturalists, and other scientists began to collectively research and address issues pertaining to global declines in biodiversity. The conservation ethic differs from the preservationist ethic, historically lead by John Muir, who advocate for protected areas devoid of human exploitation or interference for profit. The conservation ethic advocates for wise stewardship and management of natural resource production for the purpose of protecting and sustaining biodiversity in species, ecosystems, the evolutionary process, and human culture and society.
Biodiversity conservation 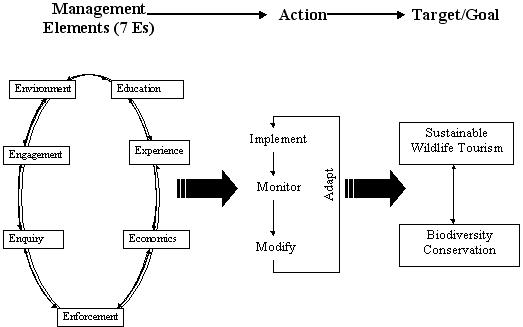 |
Conservation biologists are concerned with the trends in biodiversity being reported in this era, which has been labeled by science as the Holocene extinction period, also known as the sixth mass extinction. Rates of decline in biodiversity in this sixth mass extinction exceeds the five previous extinction spasms recorded in the fossil record. In response to the extinction crisis, the research of conservation biologists is being organized into strategic plans that include principles, guidelines, and tools for the purpose of protecting biodiversity. Conservation biology is a crisis orientated discipline and it is multi-disciplinary, including ecological, social, education, and other scientific disciplines outside of biology. Conservation biologists work in both the field and office, in government, universities, non-profit organizations and in industry. The conservation of biological diversity is a global priority in strategic conservation plans that are designed to engage public policy and concerns affecting local, regional and global scales of communities, ecosystems, and cultures. Conserving biodiversity and action plans identify ways of sustaining human well-being and global economics, including natural capital, market capital, and ecosystem services. One of the strategies involves placing a monetary value on biodiversity through biodiversity banking, of which one example is the Australian Native Vegetation Management Framework.

Conservation of Plants |

Conservation of Animals |
|



